Describe the General Characteristics of Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids
Non-metals are typically brittle and are not easily molded into shapes. Metalloids are elements having a low degree of metallic behavior.

Difference Between Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Comparison Summary Chemistry Basics Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Lessons
Metals are elements having the highest degree of metallic behavior.
. The metals form cations the nonmetals form anions and the resulting compounds are solids under normal conditions. Metalloids are either brittle or malleable and can be good conductors of heat and electricity or not. The nonmetals have higher electronegativities than do metals and compounds formed between metals and nonmetals are generally ionic in nature because of the large differences in electronegativity between them.
Metals such as silver and copper are great conductors of electricity. MetalSs and non-metals are opposite in nature but metalloids are somewhat in between the metal and non metalie. Metalloids share characteristics of both metals and non-metals and are also called.
A series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Metalloids are metallic-looking brittle solids that are either semiconductors or exist in semiconducting forms and have amphoteric or weakly acidic oxides. Difference Between Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Definition.
Example non-metal elements are Hydrogen and Carbon. Metals are also good conductors of electricity. Examples of metals are Gold Silver Iron Uranium and Zinc.
Describe the preparation properties and compounds of boron and silicon. Properties of Metals Metals are usually solids at room temperature. And have acidic oxides.
The nonmetals are elements located in the upper right portion of the periodic table. Typical nonmetals have a dull appearance relatively low melting points boiling points and densities and are poor conductors of heat and. Metals are great heat and electricity conductors and are malleable can be hammered into sheets and ductile can be drawn into wire.
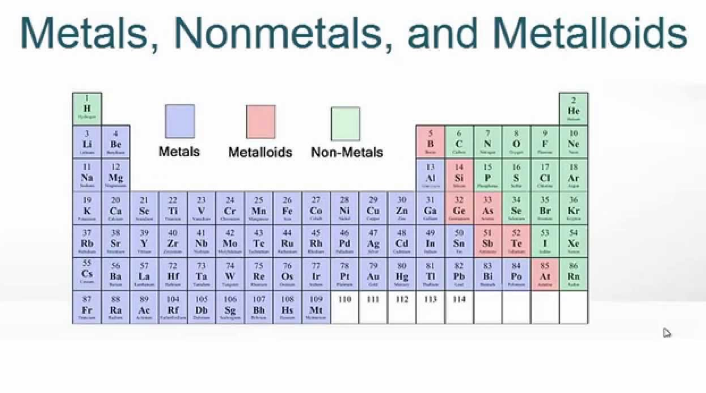
Metals non-metals and metalloids. Position in the Periodic Table. Gallery Elegant three used alkali photographs taken this month I loved this image of used alkali physical Very nice work photo of alkali physical alkaline earth Neat physical alkaline earth nonmetals image here check it out Alkaline earth nonmetals four photos taken in 2015.
Metals metalloids and nonmetals worksheet. This semi-conducting property makes Metalloids very useful as a computer chip material. As you can see most of the elements on the table are considered medals.
Make sure to use your own words 2. Next we have non metals which are indicated in yellow on this table and non metals. Describe how the properties of the different types of elements metals nonmetals metalloids differ.
Non-metals are brittle and are bad conductors of heat and electricity. Elements are divided between three characteristics. Not ductile poor heatelectricity conductors brittle dull-looking most are gas at room temperature c metalloids.
Metals non-metals and metalloids can be classified as elements. Metalloids have physical properties of both metals and nonmetals. Typical nonmetals have a dull coloured or colourless appearance.
For example the pure metalloids form covalent crystals like the nonmetals but like the metals they generally do not form monatomic anions. Students will be able to. Their chemical behavior falls between that of metals and nonmetals.
Under normal conditions more than half of the nonmetals are gases one is a liquid and the rest include some of the softest and hardest of solids. Given illustrations or descriptions students will compare metals nonmetals and metalloids using physical properties such as luster conductivity or malleability. Nonmetals are elements showing less or no metallic properties.
The metalloids are boron silicon germanium arsenic antimony and tellurium. Metals are room-temperature solids except for mercury and gallium. Describe the location of the three classes of elements in the periodic table in order to illustrate a stepped line that divides metals from nonmetals list the general properties of metals and nonmetals and acknowledging common exceptions link the properties of metals and nonmetals to their uses.
Most of those non-metals occur at room temperature in two of the three states of. They are semiconductors because their electrons are more tightly bound to their nuclei than are those of metallic conductors. Compare For each of the given elements list two other elements with similar chemical properties.
Describe the general characteristics of metals nonmetals and metalloids. Explain what characteristics of metalloids are more like metals and which are more like nonmetals based on the research you conducted and the information recorded in Data Table 1 3. These elements look metallic.
Nonmetals are poor conductors of electricity. Theyre bendable Um and theyre also good conductors of heat and electricity. Metals are generally shiny ductile malleable and good conductors of heat and electricity.
Metalloids share characteristics of both metals and non-metals and are also called semimetals. Metals non metals and metalloids show different type of physical and chemical properties. Metalloids are semiconductors of heat.
Metalloids are typically semi-conductors which means that they both insulate and conduct electricity. Their properties and behavior are quite different from those of metals on the left side. Shiny solid at room temperature conduct electricity and heat malleable have luster high melting and boiling points durable b nonmetals.
Metals are malleable and are great conductors of heat and electricity. Identify each of the following as a representative element or a transition element. However they do not conduct electricity as well as.
These are some examples of metals that you can see in their pure form and all the medals are indicated in blue here on this periodic table. Examples of metalloid elements are Silicon and Boron. Nonmetals are gases or are dull brittle and poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Metalloids are semiconductors of electricity. Are brittle when solid. Physical and chemical properties of both metals and nonmetals.
It shows the properties of both metals a. Describe The General Characteristics Of Metals search trends. Non-metals do not conduct heat or electricity very well.
Are poor conductors of heat and electricity.

General Characteristics Of Metals Metalloids And Nonmetals Download Table

10 Difference Between Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids With Examples Viva Differences
Properties Of Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Engineering Choice
Comments
Post a Comment